Introduction
We often see athletes and others with meniscus injuries at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre. Meniscus injuries are a prevalent condition that affects the knee joint. In the knee, the meniscus is essential for load distribution, joint stability, and shock absorption. Mobility and function can be severely hampered by damage to this structure, especially in active people. In-depth information about meniscus injury causes, symptoms, and physiotherapy treatment will be covered in this article, along with a comprehensive rehabilitation and knee health plan.
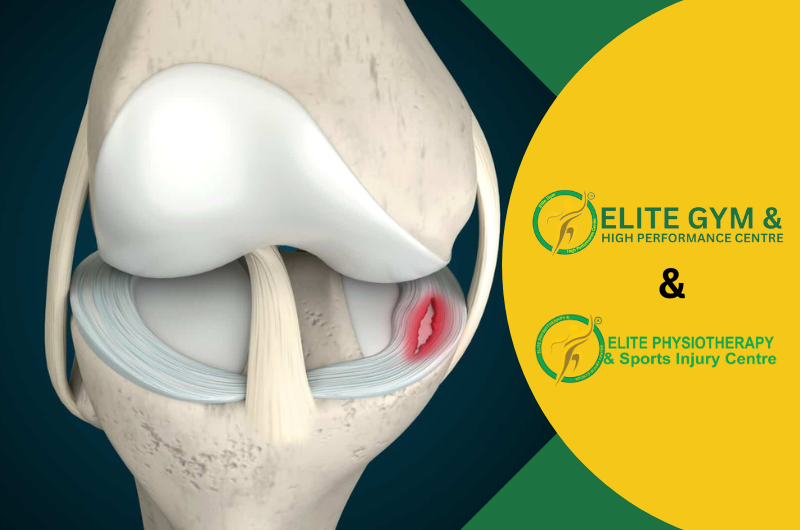
Anatomy and Function of the Meniscus
There are two menisci in the knee joint:
- Medial Meniscus (inner side): The inner side, or medial meniscus, is larger and more C-shaped.
- Lateral Meniscus (outer side): The outside side, or lateral meniscus, is smaller and rounder.
Between the tibia (shin bone) and femur (thigh bone), these fibrocartilaginous structures provide the following functions:
- Weight should be distributed over the knee joint.
- Ensure stability when moving.
- Reduce friction to preserve articular cartilage.
Causes of Meniscus Injuries
Meniscus injuries may result from:
- Trauma: Frequently experienced by sportsmen during abrupt direction changes or twisting actions (e.g., in football, basketball, or weightlifting).
- Degeneration: Wear and tear brought on by aging, which frequently causes tears in elderly people.
Symptoms of a Meniscus Injuries
- Pain localized to the knee joint.
- Swelling or effusion.
- Locking sensation or inability to fully extend the knee.
- Instability or giving way of the knee.
- Decreased range of motion and stiffness.
Diagnosis
At Elite Physiotherapy, we prioritize accurate diagnosis using:
- Clinical tests: include the Thessaly, Apley, and Murray tests.
- Imaging: MRI to verify tear type and extent.
Physiotherapy Management of Meniscus Injuries
Physiotherapy is essential for post-operative and conservative care. At Elite Physiotherapy, we prioritize function restoration, pain management, and recurrence prevention in our individualized approach.
1. Acute Phase (0–2 weeks)
Goal: The objectives are to preserve mobility, prevent joint damage, and manage pain and edema.
- Rest and Protection: Offloading weight using crutches or a knee brace.
- Pain relief: Apply ice for 15 to 20 minutes every two to three hours.
- Gentle Range of Motion (ROM) Exercises:
- Heel slips.
- Knee flexion and extension when seated.
- Isometric Strengthening:
- Quadriceps setting.
- Glutes squeezes.
2. Sub-Acute Phase (2–6 weeks)
Goals: Increase proprioception, start strength training, and improve mobility.
- Weight-Bearing Exercises: Focus on appropriate gait patterns and advance as tolerated.
- Strengthening Exercises:
- Quadriceps: terminal knee extension, straight leg lifts.
- Hamstrings: Resistance to hamstring curls and bridging.
- Glutes: Lateral band walks and clamshells.
- Proprioceptive Training:
- flat-ground single-leg stance, followed by foam pads or a Bosu ball.
3. Strengthening and Functional Training Phase (6–12 weeks)
Goal: Strengthening, stabilizing, and getting back to low-impact activities are the objectives.
- Advanced Strengthening:
- Step-ups and step-downs.
- Bulgarian split Squats.
- Leg presses (light resistance).
- Dynamic Stability:
- Side lunges from to side.
- Resistance band squats with a bosu ball.
- Balance and Proprioception:
- Single leg balance with perturbations.
- Training on a wobble board.
4. Return-to-Sport Phase (12 weeks and beyond)
Goals: Restoring complete function, agility, and sport-specific motions are the objectives.
- Plyometric Training:
- Plyometric exercises include lateral hops, box jumps, and skipping.
- Agility Drills:
- exercises for agility include cutting techniques, ladder exercises, and shuttle runs.
- Sport-Specific Conditioning:
- Under controlled circumstances, mimic motions that are pertinent to the athlete’s discipline.
Post-Surgical Physiotherapy Management
The strategy is customized for the surgical process when surgery is required (such as meniscectomy or meniscus repair):
- Meniscus Repair: To preserve the sutured tissue, a slower pace of healing is necessary. In contrast to a partial meniscectomy, weight-bearing, and range-of-motion activities are postponed.
- Partial Meniscectomy: The goal of a partial meniscectomy is to quickly restore function and movement.
Similar steps are followed in rehabilitation, although it frequently takes longer to guarantee tissue recovery.
Additional Modalities at Elite Physiotherapy
We use cutting-edge methods to improve recovery:
- Manual therapy: patellar and soft tissue mobilizations.
- Electrotherapy: ultrasound or TENS to reduce edema and discomfort.
- Dry Needling: To increase blood flow and relieve tense muscles.
- Kinesiology Taping: For proprioceptive feedback and joint support.
Conclusion
Our goal at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre is to provide the best possible care for meniscus issues. We assist people and athletes in regaining the strength, mobility, and self-assurance necessary to perform at their peak through an organized, research-based physiotherapy program.
If you’re experiencing knee discomfort or suspect a meniscus tear, reach out to us now. Together, we will create a customized rehabilitation program based on your objectives and needs.