A knee overuse injury known as Sinding Larsen Johansson Syndrome (SLJS) is more common in teenagers who do sports that require repetitive stress, such as running and jumping. We at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre are experts in identifying and managing conditions like SLJS, guaranteeing our patients a successful and individualized recovery process.
Cause and Mechanism of Injury
Repetitive tension on the patellar tendon, which connects to the patella’s lower pole (kneecap), causes SLJS. Particularly during times of rapid growth when bones and tendons are expanding at various rates, this ongoing stress causes inflammation and microtrauma. Young athletes playing high-impact sports like basketball are a classic example, since their frequent jumping puts significant strain on their knee extensor mechanism, leading to SLJS.
Signs and Symptoms
Patients with SLJS may experience:
- Localized anterior knee pain at the patella’s base that gets worse when you run, jump, or climb stairs.
- Tenderness and swelling near the patellar tendon insertion site.
- Restricted knee movement as a result of discomfort, which could cause a noticeable limp.
- Pain upon palpation of the affected area.
Diagnostic Methods at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre
Our comprehensive assessment includes:
- Detailed Patient History: Compiling a thorough patient history includes learning about the beginning of symptoms, activity levels, and any recent growth surges.
- Physical Examination: Examining posture, walking, and knee function using particular tests.
- Functional Assessment: Determining deficiencies by evaluating the knee’s strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
Special Physiotherapy Tests:
- Clarke’s Test: In order to identify pain suggestive of patellofemoral dysfunction, Clarke’s Test involves applying pressure to the superior aspect of the patella while the patient contracts the quadriceps.
- Patellar Compression Test: The patellar compression test is used to detect pain related to problems with the patellar tendon by pressing the patella against the femur.
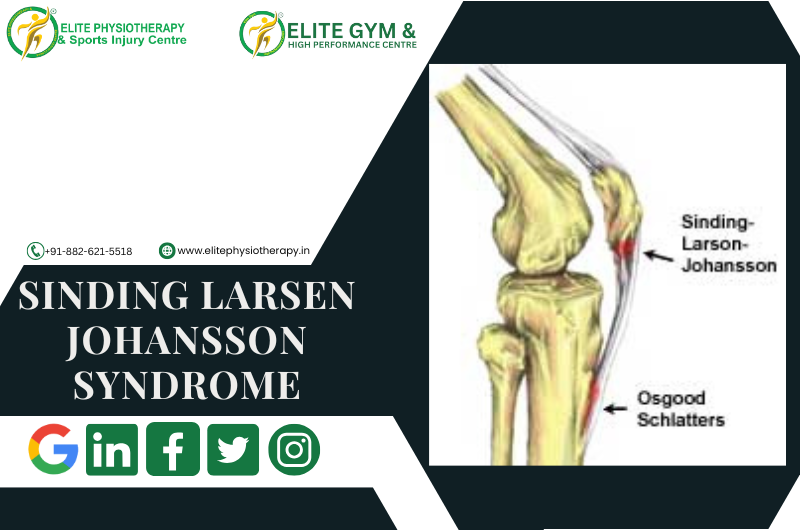
How Osgood-Schlatter disease is different from Sinding-Larsen-Johansson Syndrome
1. Location of the Issue
Osgood-Schlatter Disease (OSD):
Affects the tibial tuberosity, where the patellar tendon inserts on the tibia (shinbone).
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson Syndrome (SLJS):
Involves the inferior pole of the patella, where the patellar tendon attaches to the bottom of the kneecap.
2. Cause and Mechanism
OSD:
Caused by repetitive stress leading to microtrauma at the tibial tuberosity. Excessive pulling by the quadriceps through the patellar tendon results in inflammation and, in some cases, bone fragmentation.
SLJS:
Caused by repetitive traction forces at the inferior pole of the patella, leading to inflammation, microtrauma, or calcification in this area.
3. Clinical Features
OSD Symptoms:
- Pain and swelling over the tibial tuberosity.
- Tenderness or prominence at the tibial tuberosity (a bony bump may form).
- Pain aggravated by running, jumping, or kneeling.
SLJS Symptoms:
- Pain and tenderness at the inferior pole of the patella.
- Swelling and discomfort during knee extension activities like squatting or jumping.
- Pain on palpation directly under the patella.
Physiotherapy Management of Sinding Larsen Johansson Syndrome at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre
Our tailored treatment approach focuses on alleviating pain, reducing inflammation, and restoring function through:
1. Activity Modification: Counseling patients to temporarily stop running and jumping, as these activities aggravate symptoms, in order to promote healing.
2. Cryotherapy: Using ice packs on the afflicted area to reduce pain and swelling.
3. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises:
- Quadriceps and Hamstring Stretching: Stretching the hamstrings and quadriceps can improve flexibility and lessen patellar tendon strain.
- Strengthening exercises: To support the knee joint and increase general lower limb strength, concentrate on the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles.
4. High-End Modalities:
- Shock Wave Therapy: Using acoustic waves to encourage tissue healing and lessen pain.
- Capacitive Resistive Energy Transfer (CRET) Therapy: Using electromagnetic radiation to promote tissue regeneration and reduce inflammation is known as capacitive resistive energy transfer, or CRET, therapy.
- Super Inductive System: The Super Inductive System reduces pain and activates muscles by stimulating neuromuscular regions with high-intensity electromagnetic fields.
- High-Intensity Class IV Laser Therapy: This method speeds up healing and reduces pain by penetrating deep tissues with laser light.
- Hydrotherapy: Performing exercises in a warm pool to increase flexibility and strength while lowering joint tension.
- Cryotherapy: Using cold therapy methods to efficiently treat acute pain and inflammation.
5. Patellar Taping or Bracing: By supporting the patella, patellar taping or bracing lessens the strain on the tendon while performing daily tasks.
6. Patient education: Providing direction on appropriate biomechanics, guidelines for a phased return to sports, and recurrence prevention techniques.
Why to choose Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre
Our multidisciplinary team at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre is committed to providing individualized care, utilizing cutting-edge modalities to promote the best possible recovery for those with Sinding-Larsen-Johansson Syndrome. Our dedication to quality guarantees that every patient receives a thorough treatment plan customized to meet their unique requirements, facilitating a prompt and secure return to their preferred activities.