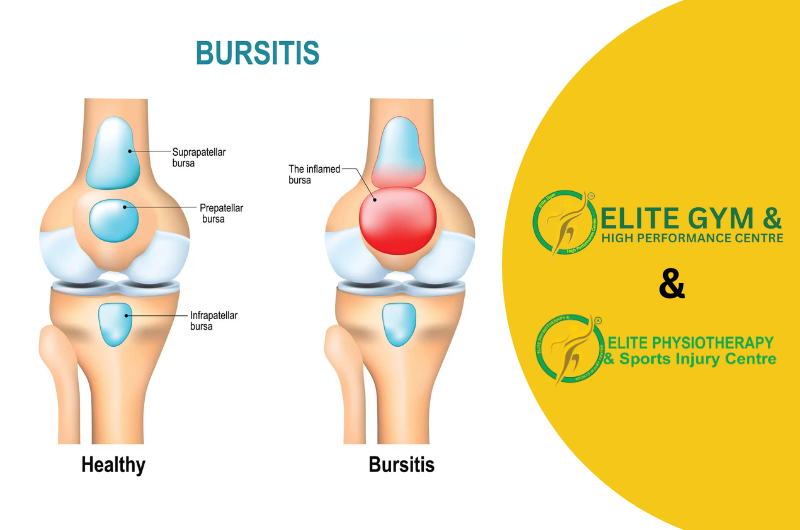
Inflammation of one or more bursae around the knee joint is a defining feature of knee bursitis. Small, fluid-filled sacs called bursae reduce friction between tissues including skin, muscles, tendons, and bones. Around the knee, there are several bursae, each with a distinct function and a connection to certain injuries or activities. For the best recovery, we at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre place a strong emphasis on a thorough approach to knee bursitis diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation.
Anatomy of the Knee Bursae
The knee joint has several bursae, each named based on its location or related structure:
1. Prepatellar Bursa
Location: In front of the patella or kneecap.
Function: Facilitates easy mobility between the skin and the patella, which is essential for those who often kneel.
Typical Reasons for Bursitis: frequently impacted by direct trauma or extended kneeling (e.g., “carpenter’s knee” or “housemaid’s knee”).
2. Infrapatellar Bursa
Location: Below the kneecap, this structure is separated into the superficial and deep infrapatellar bursae.
Function: Its purpose is to act as a cushion between the patellar tendon and the supporting tissues.
Common Causes of Bursitis: Usually brought on by frequent jumping or kneeling, commonly seen in athletes, leading to “jumper’s knee.”
3. Suprapatellar Bursa
Location: Between the femur and the quadriceps tendon, above the kneecap.
Function: During knee flexion and extension, it helps the quadriceps tendon glide smoothly over the femur.
Typical Reasons for Bursitis: This may be brought on by inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, excessive usage, or repetitive stress.
4. Pes Anserine Bursa
Location: Near the insertion of the pes anserine tendons (sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus), on the inside of the knee, beneath the joint line.
Function: Lessens friction between the underlying bone and the tendons.
Common Causes of Bursitis: common among athletic and overweight people, especially those who have valgus knee alignment (knock-knee) or tight hamstrings.
5. Semimembranosus Bursa
Location: Close to the semimembranosus tendon in the rear of the knee.
Function: Keeps the semimembranosus tendon and other structures from rubbing against one another.
Typical Reasons for Bursitis: frequently happens as a result of prolonged kneeling, severe bending, or repetitive strain from activities like jogging.
6. Iliotibial Bursa
Location: In the space between the lateral femoral condyle and the iliotibial (IT) band.
Function: Makes it possible for the IT band to move smoothly across the femur, which is crucial for bikers and runners.
Typical Reasons for Bursitis: linked to repeated stress-induced IT band syndrome, especially in endurance athletes.
7. Fibular Collateral Ligament-Biceps Femoris Bursa
Location: On the lateral side of the knee, between the biceps femoris tendon and the fibular collateral ligament.
Function: Prevents contact between the biceps femoris tendon and the fibular collateral ligament.
Typical Reasons for Bursitis: frequently impacted in sports like tennis or soccer that need quick changes or lateral mobility.
Symptoms of Knee Bursitis
Depending on the particular bursa affected, knee bursitis symptoms might vary, however, they often include:
- Localized Pain and Tenderness: Pain that is exclusive to the area where the bursa is inflamed.
- Swelling: Prominent knee swelling that is frequently warm to the touch.
- Restricted Mobility: Swelling and pain limit range of motion.
- Redness: There may be redness and inflammation in the skin surrounding the injured bursa.
Diagnosis at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre
At Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre, a detailed assessment involves:
- Clinical evaluation: a physical assessment to pinpoint the precise location and kind of discomfort.
- Imaging: Inflamed bursae can be seen using ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), particularly if the disease is persistent or does not improve with first-line therapy.
Management and Rehabilitation
1. Initial Management:
RICE (Relaxation, Ice, Compression, and Elevation) These simple actions aid in managing acute discomfort and reducing edema.
2. Drug-Based Therapies
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications, or NSAIDs, are frequently used to treat pain and inflammation.
- In extreme situations, corticosteroid injections may be used to treat chronic inflammation.
3. Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Center’s Physiotherapy Treatment
Manual therapy: Methods like soft tissue mobilization can assist increase blood flow to the injured region and lessen edema.
Electrotherapy: Techniques like TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) and ultrasound can help reduce pain and promote quicker recovery.
Therapeutic Exercises:
- Strengthening: To unload the injured bursa, focus on building up the surrounding muscles, such as the hamstrings, quadriceps, and hip stabilizers.
- Stretching: To reduce tension on certain bursae, stretch tense muscles, particularly the quadriceps, hamstrings, and IT band.
- Balance and Proprioception: Exercises for knee stability are essential for balance and proprioception, particularly for bursitis in the pes anserine and fibular collateral ligament-biceps femoris areas.
- Activity Modification: Teaching patients how to avoid stressful activities and how to stand up straight, especially when working or playing sports
4. Advanced Therapy
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy: It helps in pain reduction and promotes recovery.
High-Intensity Class 4 Laser: Helps to increase circulation at the affected area for faster recovery.
Preventive Measures
Knee bursitis may be avoided by using techniques like:
- Appropriate Training Methods: Motivating athletes to maintain balanced muscular strength and proper biomechanics.
- Gradual Progression: Steer clear of abrupt increases in exercise intensity, especially while participating in repetitive knee-bending sports.
- Proper Warm-Up: Ergonomics and Proper Footwear: Proper knee support and footwear can assist the distribution of stresses uniformly throughout the knee joint. You may lessen the strain on your knee bursae by properly warming up before exercising.
- Frequent Stretching and Strengthening: By preventing muscular imbalances, a regular stretching and strengthening regimen helps lessen the strain on particular knee tissues.
Conclusion
Our customized treatment plan for knee bursitis at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre blends state-of-the-art technology with tried-and-true therapeutic techniques to promote the best possible recovery and avoid recurrence. Our goal is to treat pain, restore function, and improve overall knee stability by attending to the individual needs of each patient. This will allow patients to confidently return to their everyday activities or sports.