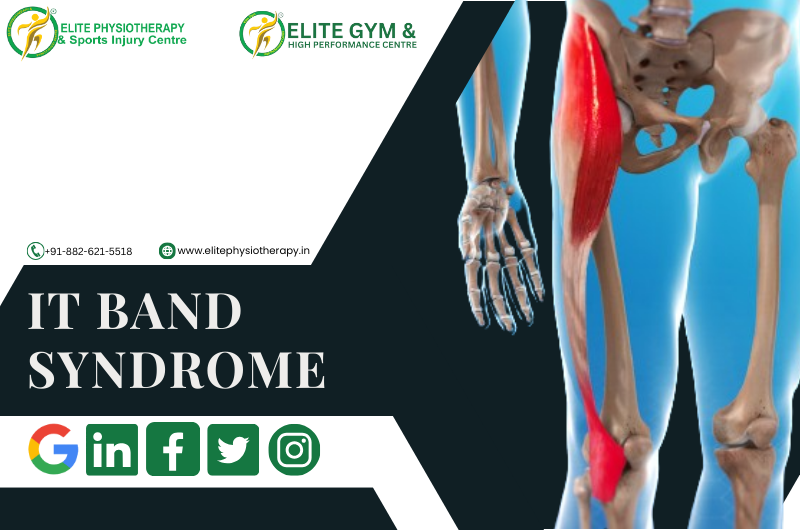
IT Band Syndrome, also known as Iliotibial Band Syndrome, is a common overuse injury that affects athletes, especially runners, bikers, and those who engage in repetitive lower-limb exercises. We at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre are experts at identifying and successfully treating this illness, enabling athletes to resume their best performance.
Causes of IT Band Syndrome
The iliotibial (IT) band is a thick band of connective tissue extending from the hip to the shinbone along the outside of the thigh is called the iliotibial (IT) band. When this band irritates or inflames as a result of excessive contact against the lateral femoral condyle, it can lead to IT Band Syndrome. Typical reasons include:
- Overuse: Running, cycling, and rowing are examples of repetitive knee flexion and extension exercises.
- Biomechanical imbalances: Include differences in leg length, weak hip abductors, or poor foot arch mechanics.
- Inappropriate training methods: Include abrupt increases in mileage, effort, or footwear.
- Tight IT Band or Surrounding Muscles: The glutes, quadriceps, or hamstrings are less flexible when the IT band or surrounding muscles are tight.
Mechanism of Injury
IT Band Syndrome can result from both on-field and off-field activity. For example, because of insufficient hip stability, a sprinter pushing off quickly during a race may overload their IT band, resulting in microtrauma and ultimately inflammation. Similarly, the IT band may rub too much against the femur if you cycle repeatedly while sitting at an incorrect height.
Signs, Symptoms, and Clinical Features
People with IT Band Syndrome frequently exhibit the following symptoms and indicators:
- Running or cycling exacerbates lateral knee pain, which is usually acute or burning.
- Sensitivity along the IT band, especially in the area next to the knee.
- Localized inflammation or swelling on the knee’s lateral side.
- Discomfort when sitting for extended periods of time or when going downstairs.
- When moving, there is an audible snapping or popping sound on the outside of the knee.
Diagnostic Methods at Elite Physiotherapy
To identify the underlying cause of IT Band Syndrome, our diagnostic method combines specific physiotherapy tests with thorough physical and functional evaluations:
1. Physical Assessment:
- Examination of posture and gait.
- Palpation along the IT band to detect discomfort.
- Assessing the hip, knee, and ankle joints’ range of motion and flexibility.
2. Functional Assessment:
- Evaluation of the mechanics of cycling or running.
- Hip abductors, glutes, and quadriceps strength tests.
3. Special Physiotherapy Tests:
- Ober’s Test: Assesses the tightness of the IT band.
- Noble Compression Test: When knee flexion and extension are performed, the Noble Compression Test detects discomfort or crepitus at the lateral femoral condyle.
- Modified Thomas Test: The modified Thomas test evaluates hip flexor and IT band flexibility.
Physiotherapy Management at Elite Physiotherapy
We at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre provide a thorough physiotherapy technique that is customized to meet the needs of every patient. In addition to treating underlying biomechanical abnormalities and symptom relief, we also aim to avoid recurrence. This is how we go about it:
1. Pain Management:
- Cryotherapy: Applying ice to alleviate pain and inflammation is known as cryotherapy.
- Electrotherapy: Techniques such as TENS or ultrasound that aid in pain management and recovery.
2. Manual Therapy:
- Soft Tissue Mobilization: Deep tissue massage to relieve tensor fasciae latae (TFL), glutes, and IT band tension.
- Myofascial Release: Targeting trigger points along the IT band and surrounding muscles is known as myofascial release.
- Joint Mobilization: Enhancing the ankle, knee, and hip joints’ alignment and range of motion is known as joint mobilization.
3. Stretching Exercises:
- Stretches that increase the flexibility of the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and IT band can be both dynamic and static.
- Examples include: The standing hip flexor stretch, pigeon position, and the cross-body IT band stretch.
4. Strengthening Exercises:
Targeted workouts to improve stability and address muscular imbalances:
- Clamshells: To strengthen the gluteus medius, use clamshells.
- Lateral Band Walks: Strengthens the hip abductors with lateral band walks.
- Single-Leg Deadlifts: Improves synergy between the glutes and hamstrings.
- Step-ups: Increase the general strength and stability of the lower limbs.
5. Biomechanical Correction:
- Postural corrections and gait retraining are used to maximize movement patterns.
- Suggestions for appropriate footwear or, if required, orthotics.
6. Return-to-Sport Training:
- Utilizing sport-specific drills to gradually resume running, cycling, or other sports.
- Exercises involving plyometry and agility can improve performance while lowering the risk of injury.
Example: IT Band Syndrome in a Cyclist
Think of a professional cyclist who gets lateral knee pain when training hard. We would evaluate their pedaling mechanics and bike fit at Elite Physiotherapy. In addition to physiotherapy treatments, we would address concerns such as incorrect saddle height or cleat position. The cyclist can resume training pain-free and more effectively with the use of focused manual treatment, stretching, and strengthening exercises.
Why Choose Elite Physiotherapy?
At Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre, we combine clinical expertise with state-of-the-art facilities to deliver personalized care. Whether you’re a professional athlete or a recreational enthusiast, our evidence-based approach ensures effective recovery and optimal performance. Visit us to experience the best in sports injury management!