Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT): Revolutionizing Pain Management at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre
In the field of physiotherapy, extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) has become a ground-breaking treatment that gives patients with musculoskeletal disorders and chronic pain hope. At Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre, we proudly incorporate this cutting-edge therapy into our comprehensive treatment plans, delivering unmatched care to our patients.
What is Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy?
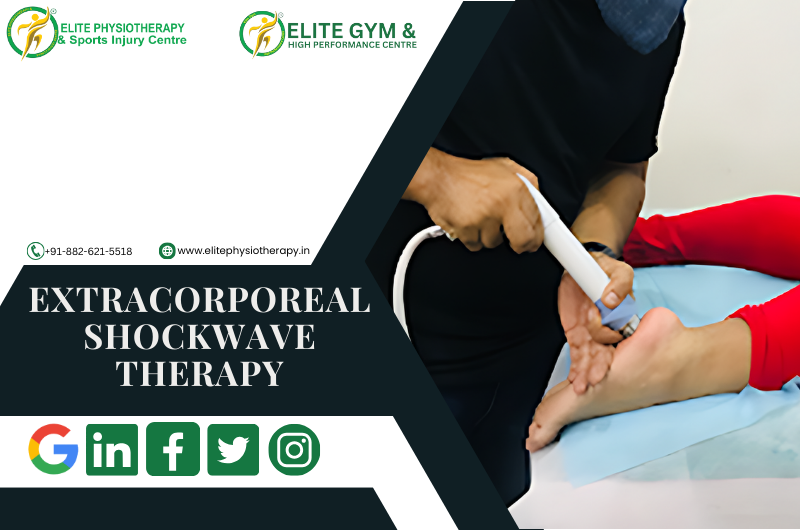
ESWT is a non-invasive procedure that uses acoustic waves to promote tissue healing, lessen discomfort, and increase range of motion. Originally developed to dissolve kidney stones, this method has been adapted to treat various sports and orthopedic conditions. Deeply penetrating the afflicted area, the high-energy sound waves encourage tissue regeneration, collagen synthesis, and blood circulation.
Conditions Treated with Shockwave Therapy
At Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre, we use ESWT to treat a wide range of conditions, including:
- Plantar Fasciitis: Chronic heel discomfort brought on by plantar fascia inflammation is known as plantar fasciitis.
- Tennis and Golfer’s Elbow: Tendinopathies brought on by repeated strain on the elbow tendons are known as tennis and golfer’s elbow.
- Shoulder Calcific Tendonitis: Pain and stiffness are caused by calcium buildup in the shoulder tendons.
- Achilles Tendinopathy: Achilles tendinopathy causes pain and inflammation in the Achilles tendon.
- Patellar Tendinopathy: Patellar tendinopathy, commonly known as jumper’s knee, is a common condition in sports.
- Myofascial trigger points: Excruciating muscular knots that limit range of motion.
- Shin Splints: Overuse or stress-related pain along the shin bone.
Shockwave therapy effectively treats many other sports and musculoskeletal injuries beyond the conditions listed above..
How ESWT Works
The therapy uses a specialized device to deliver focused or radial shockwaves to the affected area. These shockwaves accelerate the body’s natural healing processes by:
- Increasing blood flow to the area.
- Improving the mechanics of cellular repair.
- Breaking down calcified deposits.
- Desensitizing nerve endings to lessen pain.
The treatment requires no anesthesia or recovery time and takes place in brief sessions, typically lasting 15 to 20 minutes. After three to five sessions, the majority of patients report notable improvements.
Why Choose Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre for ESWT?
To achieve the best outcomes, we at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre mix state-of-the-art equipment with individualized treatment. What makes us unique is this:
- Expert Team: Our physiotherapists stay updated on the latest ESWT procedures to deliver safe and efficient therapy.
- Holistic Approach: To address the underlying source of pain, we combine ESWT with other evidence-based treatments such as manual therapy, exercise rehabilitation, and recovery sessions like ice baths, hydrotherapy, etc.
- Patient-Centered Care: We customize each treatment program to match the patient’s needs, objectives, and lifestyle.
- Modern Equipment: Our clinic has state-of-the-art ESWT equipment, which guarantees accurate and effective care.
Benefits of ESWT
There are several advantages for patients receiving ESWT at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre, such as:
- Pain relief: A notable decrease in persistent pain that doesn’t require medicine.
- Faster Recovery: Injured tissues heal more quickly.
- Better Mobility: Restoring function and movement in afflicted areas.
- Non-Invasive: A risk-free, minimally invasive surgical substitute.
Your Journey to Pain-Free Living Starts Here
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy may provide the answer you need for chronic pain or a sports injury. Our goal at Elite Physiotherapy and Sports Injury Centre is to assist you in achieving both peak performance and long-lasting relief.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a healthier, pain-free life.